Our Manufacturing Services
Due to our high degree of specialization in CNC machining and all necessary post-processing, we can realize excellent quality, outstanding conditions and first-class logistics for your machined parts.
CNC milled parts are precision components produced by removing material from a solid workpiece using computer-controlled rotary cutting tools, enabling tight tolerances and complex geometries. They are widely used across industries for functional prototypes, end-use components, fixtures, and high-accuracy mechanical assemblies where reliable fit, strength, and repeatable quality are required.
CNC Turning
CNC turned parts are precision components manufactured by rotating a workpiece in a lathe while computer-controlled tools remove material to create accurate cylindrical, conical, and threaded geometries. They are commonly used across industries for shafts, bushings, pins, sleeves, connectors, and other rotationally symmetric parts where consistent dimensions, smooth surfaces, and repeatable performance are required.
Post-Processing
Post-processing for CNC milled and turned parts includes surface finishing and functional treatments such as deburring, blasting, polishing, anodizing, plating, passivation, heat treatment, and coating to improve appearance and performance. These processes enhance corrosion and wear resistance, adjust hardness, reduce friction, improve fatigue behavior, and ensure parts meet dimensional, cleanliness, and surface-quality requirements for reliable use in demanding applications.
A Prequalified CNC-Manufacturing Network
to get your Parts Machined
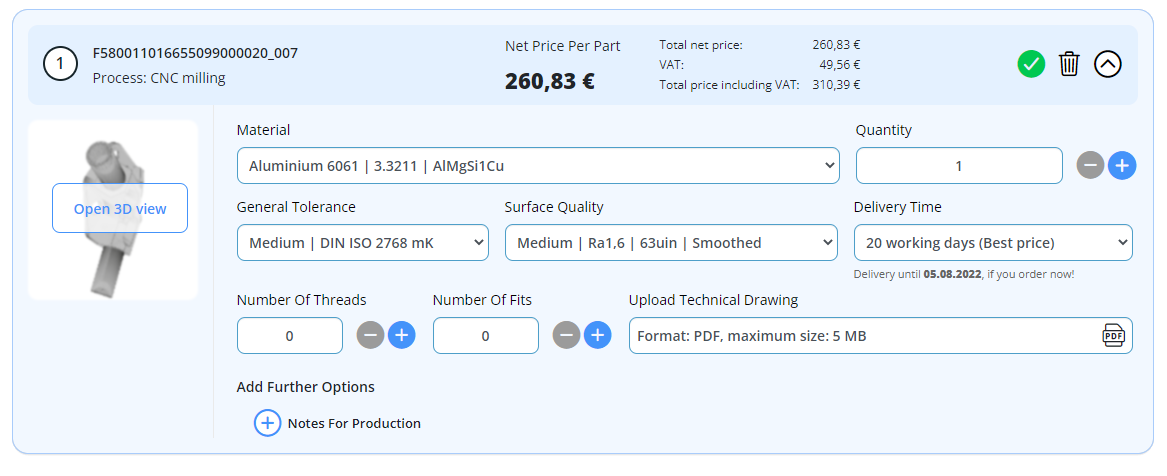
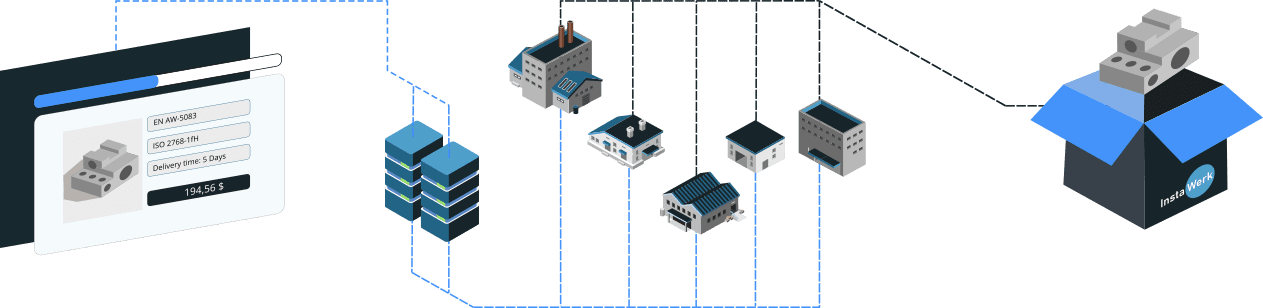
You can conveniently place your order via our online calculation for turned or milled parts. We will take care of quality, production monitoring and logistics right to your desk.
Instant
Quoting
Upload your parts to our online calculator and get an instant quote for your CNC machined parts. Your Data is saved and processed on ISO 27001 certified servers.
Precision
Manufacturing
Our intelligent matching algorithm assigns your parts to the highest quality available CNC-manufacturer. Your data is never visible to other manufacturers.
Express
Shippment
We take care of quality control, shipping and customs for you. You simply get perfect CNC components – without any annoying administrative processes.
Scalable CNC-Manufacturing with Quality in Mind
You cannot optimize the manufacturing triangle of time, cost and quality within one manufacturing facility. Therefore, we leverage our network of over 1,000 suppliers to realize the highest availability, attractive conditions and high-precision CNC components for you.
Reliable Manufacturing Capacities
By permanently tracking the reliability and quality of our suppliers, we ensure a highly resilient, reliable and high-quality network of CNC manufacturers.
From Prototypes to Serial Manufacturing
Whether it’s one piece or several thousand, at InstaWerk we ensure a high level of scalability so that you can securely and cost-effectively source your CNC-machined parts from development to market launch.
Quality, Quality, Quality
We are not just about accessibility and competitive offers. We are concerned with outstanding quality that is accessible and affordable. To achieve this, we develop in-depth quality standards and processes.
Unbeaten Conditions
By bundling orders into large order volumes, using network effects and streamlining all processes through digitalization, we offer unbeatable conditions for your CNC components.
Instant Pricing Feedback
Why wait weeks for quotes? At InstaWerk, you can get your instant quote for CNC manufacturing in seconds. Our pricing is based on AI, empirical data from previous projects and considers the current market environment.
Choose the ideal setup.
You will always find the right setting for your project via the flexible choice of materials, delivery times and quality requirements.
Add what you need.
Add post treatments, quality certificates or express delivery and only pay for what you actually need.
f.a.q.
CNC manufacturing can raise complex issues. Or be quite simple.
CNC machined parts are all about precision. Therefore, we have aligned all our processes to the highest quality standards. Our goal is to make German-level quality available at attractive conditions.
At InstaWerk, the customer comes first: That’s why we design our processes with a clear customer focus. Ordering turned and milled parts from InstaWerk is simple, cost-effective and fast. Through our digital processes and a high degree of automation, we streamline ordering processes and can pass on the cost advantage directly to our customers. An important building block for this is our online calculation, which you can use to calculate and order your turned parts and milled parts 24 hours a day.
The quality of the components is key. That’s why we run a closed manufacturing network to keep your data safe and ensure high quality production. Due to our unique order bundling, we can allocate higher order volumes to our CNC manufacturers and realize competetive pricing. In this way, we are able to reconcile low costs for our customers with the highest quality components.
First, all manufacturing partners go through an accreditation process in which we evaluate the manufacturing capabilities, quality processes and technical capabilities. Only CNC manufacturers that meet our high quality standards are accepted into the manufacturing network.
We also operate a closed manufacturing network. This means that manufacturers cannot freely join the network and cannot view projects.
Using our data analysis capabilities and the experience gained from thousands of manufacturing projects, we can motivate excellent finishers with more orders and exclude below-average finishers from the network using key performance indicators. SO successively increases our platform quality.
In order to further develop our manufacturing partners, we promote a culture of open communication, regular quality audits and processes for continuous quality improvement.
We provide prototypes as well as series parts. Online calculation is particularly suitable for prototypes and smaller quantities. Here you can use your CAD model to calculate various configurations of your turned and milled parts and order them directly online.
For series parts with larger quantities or milled parts with special alloys, on the other hand, the inquiry via contact form is the best option. We will review your data and will be happy to provide you with an offer. Our engineering team also takes care of all in-depth questions for series inquiries.
In times of increasing uncertainty and supply shortages, instead of buying your own machines, maintaining them and hiring staff for manufacturing, so-called on-demand services offer the advantage of a more flexible, cost-effective and resilient solution. In addition, many companies recognize the value in simple, digitized processes and the ability to focus on your core business rather than chasing day-to-day manufacturing issues.
For start-ups, research institutes and other innovation drivers, the value of InstaWerk lies primarily in being able to order fast, cost-effective and highest-quality turned and milled parts conveniently and easily. This allows small teams to successfully develop innovations and bring them to market quickly.
Corporates love InstaWerk too: In addition to the unbeatable conditions, we offer digital processes, fast and uncomplicated procurement solutions, and outstanding quality. Thus, InstaWerk is becoming a preferred solution in strategic procurement for more and more larger companies.
Your data will be reviewed and approved by our team after the order. Afterwards you will receive an order confirmation with payment information from us. Then our algorithm assigns the production order to a production bundle and this is allocated to a suitable CNC-manufacturer. Your data remains protected from unauthorized access and only those who really need to see your data have access to it.
InstaWerk was founded to solve a problem we experienced first-hand at CIKONI: sourcing high-quality parts reliably and at scale, from prototypes to serial production. Suppliers were often unavailable when timelines tightened, capacity fluctuated, and quoting turned into a slow cycle of RFQs, follow-ups, and comparisons with limited transparency on quality and delivery reliability. This repeatedly slowed down engineering work and added avoidable risk to project schedules. We built InstaWerk to replace that friction with a faster, more predictable approach: instant quotes combined with controlled execution, an exclusive pre-audited partner network, ISO 9001 certified processes, and in-house inspection. Read more about InstaWerk.
CNC Machining as a Scalable System
Instant Quotes, Unlimited Capacity, Verified Quality
InstaWerk is a complete CNC machining solution – not just a place to order parts, but a system that connects instant quoting, DFM clarity, and reliable production execution. It brings engineers, procurement, and manufacturing onto one streamlined workflow with transparent pricing, lead times, and quality assurance built in. From prototype to series, you get scalable capacity, controlled supplier performance, and consistent inspection standards in one platform.
Unlimited Capacity
InstaWerk delivers access to over 2.500 Machines for CNC-milled parts and CNC-turned parts, giving engineers and procurement specialists all the ressources they need instantly. With over 60 materials and 40 post treatments and a high variety of processes there are endless possibilities for most advanced designs.
Ordered in Seconds
InstaWerk’s instant quoting gives engineers and procurement specialists immediate, reliable price and lead-time visibility for CNC machined parts, eliminating back-and-forth and accelerating design-to-order decisions. It standardizes procurement, reducing sourcing risk while keeping projects moving with faster approvals and cleaner workflows.
Express Shippment

InstaWerk is ISO 9001 certified and runs an inhouse Quality Control Hub with high-end ZEISS CMMs – every order is verified internally before shipment. All production runs through pre-audited suppliers that are continuously monitored, ensuring consistent, traceable quality from first article to series parts.
Available Materials and Post Treatments for Online Quotes
InstaWerk offers a broad portfolio of engineering materials that enables even the most demanding designs – from lightweight structures and corrosion-critical components to wear-focused parts and high-performance assemblies. This range helps you align your CNC machined parts with real-world requirements like strength, weight, chemical exposure, temperature, and long-term durability. The materials listed in this section reflect our current standard offering for CNC milled parts and CNC turned parts. If you need a material that is not shown here, InstaWerk can usually source it via individual request, so you can still match your design to the exact application needs.
Available Materials for CNC Machining
Aluminium At InstaWerk, aluminium is a go-to choice for CNC milled parts and CNC turned parts when low weight, corrosion resistance, and strong value for money matter. Typical applications include housings, brackets, structural parts, and functional components across machinery, automotive, and electronics. Commonly used alloys include EN AW-6061 and EN AW-6082 – both reliable options for lightweight CNC machined parts with solid mechanical performance.
AlMg1SiCu (EN AW-6061, 3.3211) is a widely used aluminium for CNC machining of brackets, housings, frames and lightweight structural components, especially where both CNC milled parts and CNC turned parts need good dimensional stability. Advantages include very good machinability, a strong strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and consistently clean surface finishes in CNC Milling and CNC Turning. Disadvantages are lower hardness and wear resistance than steels, limited suitability for high-temperature load cases, and a tendency for thin sections to vibrate if the setup is not rigid.
AlZn5,5MgCu (EN AW-7075, Ergal, 3.4365) is used for high-performance CNC machined parts such as load-critical brackets, precision mounts, structural connectors and high-strength shafts, often as CNC milled parts with occasional CNC turned parts where maximum strength-to-weight matters. Advantages are very high strength and stiffness for aluminium plus strong fatigue performance, enabling lightweight designs that would otherwise require steel. Disadvantages include weaker corrosion resistance than 6xxx/5xxx alloys, limited weldability, and higher material cost; protective finishing is often needed depending on environment.
AlMgSi1 (EN AW-6082, Anticorodal, 3.2315) is a standard choice for structural CNC machined parts like brackets, frames, plates, mounts and machined blocks, especially when you need stiff CNC milled parts and solid CNC turned parts in one build. Advantages include higher strength than many 6xxx alloys, good corrosion resistance, and generally reliable machinability for CNC Milling and CNC Turning with stable tolerances. Disadvantages are less consistent decorative surface quality compared to 6060/6063 (not ideal for premium anodized cosmetics) and a higher risk of distortion on thin or highly relieved geometries if residual stresses are present.
AlMg0,7Si (EN AW-6063, 3.3206) is often chosen for CNC machining of lightweight profiles, covers, trim parts and functional housings where good surface quality matters for CNC milled parts and simple CNC turned parts. Advantages include excellent corrosion resistance, very good anodizing response for decorative finishes, and stable behavior in CNC Milling when cutting loads are moderate. Disadvantages are lower strength than EN AW-6061 and a higher sensitivity to deformation on thin walls, so it is less ideal for highly loaded CNC machined parts.
AlMg2,5 (EN AW-5052, 3.3523) is commonly used for corrosion-resistant CNC machined parts such as covers, plates, marine and chemical-environment components, and lightweight fixtures, typically produced as CNC milled parts from plate and as simpler CNC turned parts from bar. Key advantages are excellent corrosion resistance (especially in saltwater), good fatigue performance for its class, and reliable results in CNC machining when surface finish is prioritized over maximum strength. Disadvantages are lower strength and hardness than 6xxx alloys, plus a more “gummy” cutting behavior that can increase burrs and built-up edge, making very sharp edges and tight cosmetic requirements more demanding.
AlCuMgPb (EN AW-2007, 3.1645) is a classic choice for high-precision CNC machining of fasteners, fittings, shafts and connector-style components, especially when producing large volumes of CNC turned parts with tight tolerances. Its main advantages are outstanding machinability, excellent chip breaking and high strength, which enables fast cycle times and very consistent CNC machined parts in CNC Turning. Downsides are comparatively weak corrosion resistance and limited suitability for welding or decorative anodizing, plus the lead content can trigger compliance restrictions depending on industry and destination market.
AlCuMg1 (EN AW-2017A, 3.1325) is frequently used for load-bearing CNC machined parts like brackets, structural connectors, plates and precision components where higher strength than 6xxx aluminium is needed in CNC milling and occasional CNC turned parts. Advantages include high strength, good fatigue performance and reliable dimensional stability, making it suitable for mechanically stressed CNC milled parts. Disadvantages are reduced corrosion resistance compared to 5xxx and 6xxx alloys, and anodizing quality is typically less uniform, so it is not ideal for decorative surfaces without additional protection.
AlCu4Mg1 (EN AW-2024, 3.1355) is a high-strength aerospace-grade aluminium used for heavily loaded CNC machined parts such as structural brackets, rib-like components, precision plates and performance-critical fittings, typically produced as CNC milled parts and occasionally as CNC turned parts. Advantages are excellent strength-to-weight ratio and strong fatigue behavior, enabling lightweight designs without moving to steel. Disadvantages include poor corrosion resistance compared to 6xxx/5xxx alloys, limited weldability and less consistent decorative finishing, so protective coatings are often required.
AlMg4,5Mn (EN AW-5083, 3.3547) is typically used for robust, corrosion-resistant CNC machined parts such as marine and offshore components, plates, brackets, base parts and pressure-related hardware, most often produced as CNC milled parts from thick plate and occasionally as CNC turned parts from bar. Advantages include excellent seawater corrosion resistance, high strength for a 5xxx alloy, and very good toughness, making it a strong choice for demanding environments in CNC machining. Disadvantages are a relatively ductile cutting behavior that can promote burr formation and built-up edge, plus it is not ideal for decorative anodizing compared to 6xxx alloys.
AlMg3 (EN AW-5754, 3.3535) is widely used for corrosion-resistant CNC machined parts such as plates, covers, brackets, panels and enclosures, especially in automotive, marine and general equipment where CNC milled parts dominate and simpler CNC turned parts are possible from bar. Advantages include excellent corrosion resistance, good toughness and weldability, plus reliable performance for medium-load applications. Disadvantages are lower strength than many 6xxx/2xxx alloys and a more ductile “gummy” cutting behavior that can increase burrs and make crisp edges harder to achieve.
AlMgSi0.5 (EN AW-6060, 3.3206) is commonly used for CNC machined parts like lightweight housings, brackets, covers and profile-based components where good surface finish is important for CNC milled parts and straightforward CNC turned parts. Advantages include good corrosion resistance, stable machining behavior, and an excellent response to anodizing, which makes it attractive for visible CNC machined parts. Disadvantages are lower strength than EN AW-6061 and reduced suitability for highly loaded interfaces, plus thin walls can deform if clamping is aggressive.
Available Post Treatments for CNC-Machined Parts
InstaWerk offers a broad range of post treatments that let you realize demanding designs as a true one-stop solution – from targeted mechanical performance and wear resistance to corrosion protection, cleanability, and traceability. By combining CNC machined parts with the right finishing options in one workflow, you avoid coordinating multiple suppliers, reduce handovers, and keep responsibility and quality control in a single place. The treatments listed in this section reflect our current standard offering across heat treatments, surface treatments, coatings, and marking or cleaning steps. If you need a post treatment that is not shown here, InstaWerk can usually provide it via individual request, so your part can still be matched to the exact application requirements.
Heat treatments at InstaWerk are applied when CNC machined parts must hit defined mechanical performance targets – typically higher wear resistance, fatigue strength, or long-term dimensional stability in service. The most common options are hardening, stress-relief annealing, and nitriding (gas or plasma), selected based on whether you need bulk strength or a hardened functional surface.
Example: 42CrMo4 (1.7227) + nitriding for long-life shafts or sliding contact surfaces with high wear demand.
Example: 16MnCr5 (1.7131) + hardening for drivetrain-style components where a durable surface and robust core matter.
At InstaWerk, hardening is done by austenitizing the steel, quenching, and then tempering to reach a defined hardness and strength level for CNC machined parts. The upside is significantly improved strength and wear resistance, the downside is increased brittleness risk and potential distortion that must be tolerated in the design. Application-wise, define target hardness (and whether toughness or wear is the priority), and consider contact stresses, shock loads, and whether post-treatment finishing surfaces are function-critical.
Applicable materials:
– 42CrMo(S)4 – 4140 – 1.7227
– C45 – AISI 1045 – 1.0503
– 16MnCr5 – AISI 5115 – 1.7131
– X20Cr13 – AISI 420 – 1.4021
– 40CrMnNiMo8-6 – 1.2312
Stress-relief annealing at InstaWerk is performed by heating the part to a moderate temperature below transformation (or below solution ranges for non-ferrous alloys) and holding it long enough to reduce residual stresses, followed by controlled cooling. Benefits are improved dimensional stability and reduced risk of warping or cracking in service, while drawbacks include added lead time and possible slight changes in strength depending on alloy and prior condition. From an application perspective, it is most valuable for large, thin-walled, or highly relieved CNC machined parts where stability matters over peak strength.
Applicable materials:
– EN AW-6061
– EN AW-6082
– EN AW-7075
– EN AW-2024
– 42CrMo(S)4 – 1.7227
– C45 – 1.0503
– S355J2+N – 1.0570
– 40CrMnNiMo8-6 – 1.2312
– Titanium Grade 5 – 3.7165
– Copper Cu-ETP – 2.0065.
Gas nitriding at InstaWerk is a thermochemical process where nitrogen diffuses into the steel surface in an ammonia-based atmosphere, forming a hard surface layer. Pros are high surface hardness, improved wear and fatigue performance, and typically lower distortion than quench hardening. Cons are that results depend on alloy and it improves surface properties rather than bulk strength. Define required case depth, contact conditions, and whether corrosion protection is needed.
Applicable materials:
– 42CrMo(S)4 – 4140 – 1.7227
– 16MnCr5 – AISI 5115 – 1.7131
– 40CrMnNiMo8-6 – 1.2312
– C45 – 1.0503
– X20Cr13 – AISI 420 – 1.4021
Plasma nitriding at InstaWerk uses a low-pressure glow-discharge plasma to introduce nitrogen into the surface, allowing very controlled layer formation. Advantages include excellent wear resistance, good dimensional stability, and process control. Disadvantages are higher process complexity and the need to align expectations with alloy behavior and the environment. It is a strong choice for wear and fatigue-loaded parts where tight dimensional stability is important.
Applicable materials:
- 2CrMo(S)4 – 1.7227
- 16MnCr5 – 1.7131
- 40CrMnNiMo8-6 – 1.2312
- X20Cr13 – 1.4021
- X5CrNi18-10 – AISI 304 – 1.4301 (spec-dependent)
- X2CrNiMo17-12-2 – AISI 316 – 1.4401 (spec-dependent)
- X2CrNiMo17-12-2 – AISI 316L – 1.4404 (spec-dependent)
- X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 – AISI 316Ti – 1.4571 (spec-dependent)
InstaWerk delivers cost savings of up to 35% by combining competitive global sourcing with intelligent order bundling and an exclusive supplier network – in practice, customers often see around 19% lower pricing versus alternative suppliers for comparable CNC machined parts. Beyond piece price, the bigger lever is indirect cost: by standardizing specifications, consolidating vendors, and streamlining the full RFQ-to-PO workflow, teams can cut procurement effort by up to 90%. For advanced setups, procurement can be taken close to full automation via an OCI API integration, reducing manual touchpoints and cycle time while improving traceability. These savings do not trade off against quality, since parts are governed by rigorous quality control with inhouse Zeiss CMM measurement and ISO 9001-certified processes.
InstaWerk accelerates sourcing by turning RFQs into instant quotes and direct orders, cutting out the back-and-forth that typically slows down CNC machined parts procurement. Engineers get fast feasibility feedback and clear pricing upfront, while procurement benefits from a standardized, auditable ordering flow that reduces coordination overhead. Lead times start from 3 days for many CNC milled parts and CNC turned parts, helping teams keep prototypes and production ramps on schedule. For urgent needs, express delivery can be arranged from 24 hours on request, making last-minute design iterations and critical spares significantly easier to manage.
InstaWerk ensures consistently high quality for CNC Machining by combining ISO 9001-certified processes with rigorous, standardized quality gates for CNC machined parts. A dedicated in-house quality hub with Zeiss CMMs and additional high-end inspection equipment enables reliable verification of critical dimensions on CNC-milled parts and CNC-turned parts, including tight tolerances and feature-level checks. Supply is secured through an audited, exclusive supplier network, so only qualified partners manufacture your CNC machined parts to defined standards. Continuous, data-based monitoring of supplier performance adds an additional control layer, improving repeatability across batches and reducing risk for engineers and procurement teams alike.
InstaWerk focuses on what matters most for demanding hardware teams: CNC Machining – specifically CNC Milling and CNC Turning – instead of spreading attention across unrelated processes. This specialization enables eye-level, shoulder-to-shoulder communication with engineers and procurement, and equally clear alignment with suppliers, because every discussion is grounded in the realities of CNC-milled parts and CNC-turned parts. Within this domain, you get in-depth engineering support and practical process know-how to de-risk specifications, tolerance stacks, and functional requirements for CNC machined parts. With 60+ materials and 40+ post treatments, the portfolio stays highly versatile while remaining fully optimized for CNC Machining outcomes.
InstaWerk runs on software that is self-developed, self-hosted, and self-managed, which means every data flow in the ordering process is under direct control – from CAD upload to delivery of CNC-milled parts and CNC-turned parts. This reduces uncertainty about where CAD files, drawings, and order data are processed, and it supports clearer governance for engineering and procurement workflows around CNC machined parts. Strict access and data control mechanisms are in place to minimize exposure and enforce consistent handling across projects and stakeholders. The approach is designed to meet data protection law requirements and to provide a dependable foundation for companies with elevated confidentiality, compliance, or IP protection standards.
InstaWerk supports CNC Machining projects end-to-end with in-house engineering and production experts based in Germany, helping teams specify and source CNC machined parts with confidence. This experience is built on working with more than 2,500 customers across a wide range of industries, from fast-moving product development to regulated environments with strict documentation needs. A dedicated support engineer is available before, during, and after production, ensuring continuity across quoting, design clarification, supplier coordination, and delivery of CNC-milled parts and CNC-turned parts. The result is faster decisions, fewer misunderstandings, and lower project risk for both engineers and procurement.
Access our unlimited manufacturing ressources now:
Instant Quoting | Unlimited Manufacturing Capacity |
High Quality Exclusive Network | Short delivery times
Ressources on Digital Manufacturing
The CNC industry is evolving fast with an everlasting focus on precision. We keep you up to date with the latest news on CNC manufacturing and InstaWerk.